ITEM 511 CONCRETE FOR STRUCTURES
511.01 Description
511.02 Materials
511.03 Proportions
511.04 Mix
Options for Class HP.
511.05 Class HP Test Slab
511.06 Concrete Test Specimens
511.07 High Early Strength Concrete
511.08 Mixing of Concrete
511.09 Slump
511.10 Placing Concrete
511.11 Slipform Construction of Bridge Railing
511.12 Construction Joints
511.13 Work Stoppage
511.14 Depositing Concrete Under Water
511.15 Depositing and Curing Concrete During Cold Weather
511.16 Removal of Forms
511.17 Curing and Loading
511.18 Surface Finish
511.19 Roadway Finish
511.20 Bridge Deck Grooving
511.21 Sidewalk Finish
511.22 Sealing Joints and Cracks
511.23 Class HP Concrete Testing
511.24 Method of Measurement
511.25 Basis of Payment
511.01 Description. This work consists of providing falsework and forming, furnishing, placing, consolidating, finishing, and curing portland cement concrete. This work also includes diamond saw cutting transverse grooves into the surface of superstructure concrete. Construct falsework and forms as required in Item 508.
511.02 Materials. Furnish materials conforming to 499.02, except as modified below.
Use the same kind and color of aggregate for all concrete above the ground line in a given substructure unit and for all concrete in a given superstructure.
Use high molecular weight methacrylate resin sealer conforming to 705.15.
Use curing materials conforming to 705.05; 705.06 (white opaque); or 705.07;Type 1 or 1D.
Use 1/4-inch (6 mm) gray sponge joint filler conforming to 711.28, or use preformed filler conforming to 705.03.
Use preformed elastomeric compression joint seals conforming to 705.11.
511.03 Proportions. Proportion concrete for structures according to 499.03, using Class C, S, or HP as specified in the Contract.
At least 3 days before placing Class HP, including the test slab, submit, in writing, the mix design and batching sequence to the Engineer. The Engineer will review the mix design for conformance to proportion requirements, otherwise the mix design is for the Engineer’s information.
511.04 Mix Options for Class HP. Except for parapet concrete, use Class HP 3 or 4 for all superstructure concrete unless specific concrete mixes are specified. If using Class HP 3 for the deck, use Class HP 1 or 3 for all other superstructure concrete. If using Class HP 4 for the deck, use Class HP 2 or 4 for all other superstructure concrete.
For Class HP, the Engineer will waive Item 499 calendar time restrictions regarding the use of fly ash.
511.05 Class HP Test Slab. Produce a trial batch of concrete equal in size to the batch required for the concrete superstructure and conforming to the mix design. Ensure that the trial batch is workable and able to be finished.
Place an 8 ft ´ 4 ft ´ 4-inch (2.4 m ´ 1.2 m ´ 0.1 m) test slab when the atmospheric conditions approximate the conditions anticipated for placing the superstructure. Finish and texture the test slab according to this section, however, the Contractor is not required to texture the concrete using a saw.
If the Engineer determines that the trial batch is not workable or not able to be properly finished, modify the mix design or batching sequence. Submit the revised mix design and batching sequence to the Engineer, and place another test slab. Repeat the submittal and test slab process until producing a trial batch that is both workable and able to be finished. Do not place any Class HP until the Engineer accepts the test slab pour.
511.06 Concrete Test Specimens. The Engineer will make test cylinders as follows:
A. Structures over 20-foot (6.1 m) span. Two test cylinders from each 200 cubic yards (150 m3) of concrete, or fraction thereof that is incorporated into the work each day.
B. Structures of 20-foot (6.1 m) span or less. At least two test cylinders for each 50 cubic yards (35 m3) of concrete.
The Engineer will make and test concrete test beams according to Supplement 1023 when the Contractor plans to remove falsework early as specified in 511.16.
511.07 High Early Strength Concrete. If it is desirable to expedite the work, the Contractor may use high early strength cement, additional cement, approved chemical admixtures, or a combination of these materials at no additional cost to the Department. Cure and load concrete according to 511.17.
511.08 Mixing of Concrete. Mix concrete according to 499.09.
When mixed, all concrete shall have a temperature of not more than 90 °F (32 °C). Maintain the concrete under this temperature until concrete is deposited in the work.
When an air temperature of 60 °F (16 °C) or higher prevails at the time of placing concrete in a bridge superstructure over 20-foot (6.1 m) span, add a chemical admixture conforming to 705.12, Type B or D to the concrete. Use 705.12 Type, A or D for Class HP concrete in lieu of 705.12, Type B or D.
511.09 Slump. Within the slump ranges specified in 499.03, provide a slump that produces concrete that is workable in the required position, flows around reinforcing steel, and coats individual particles of coarse aggregate with mortar containing the proportionate amount of sand.
The Engineer will measure the slump according to ASTM C 143.
511.10 Placing Concrete. Submit to the Engineer a description of proposed placing procedures and notify the Engineer at least 24 hours in advance of placing concrete.
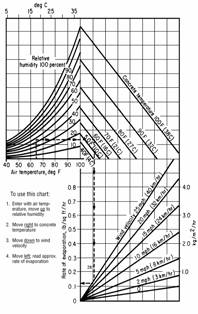
Place superstructure concrete when the ambient air temperature is 85 °F (30 °C) or less and not predicted to go above 85 °F (30 °C) during the concrete placement; and when evaporation rates, determined according to Figure 1 in ACI 308, do not exceed the following:
|
Class |
Evaporation Rate |
|
S |
0.2 pound per square foot per hour (1.0 kg/m2/hour). |
|
HP |
0.1 pound per square foot per hour (0.5 kg/m2/hour). |
Determine and document the ambient air temperature, concrete temperature, deck surface temperature, relative humidity, and wind velocity, subject to verification by the Engineer. Measure data required in Figure 1 from within 10 feet (3 m) of the area where the superstructure concrete is placed.
Figure 1 does not apply to substructure items and poured parapets. Figure 1 applies to slip-formed parapets.
To meet favorable atmospheric conditions, may require the Contractor to place concrete at night. At least 24 hours before placing concrete at night, submit a lighting plan for the work area to the Engineer. Obtain the Engineer’s approval of the lighting plan before placing the concrete. Direct lights so that approaching traffic is not affected or distracted.
Before placing a concrete deck on continuous steel beams or girders, complete all of the main beam or girder splices at least two piers beyond the pier or piers supporting the concrete.
Before placing concrete for backwalls above the approach slab seat with steel expansion joints, backfill the abutments to within 2-foot (0.6 m) of the bridge seat elevation, place superstructure concrete in the adjacent span, and either erect structural steel or prestressed concrete beams. Use the steel expansion joint as a template for the top of the backwall. If temporary bolts are used to support the backwall portion of an expansion device during the placing of the backwall concrete, remove the bolts after the concrete has taken its initial set and before a change in temperature causes superstructure movement sufficient to damage the backwall.
Before placing concrete, assure the Engineer of an adequate and uniform source of supply of concrete to allow proper placing and finishing, and of the availability of coverings to protect the concrete from rain.
Do not add or apply water to the concrete after it has left the truck and before applying curing materials according to 511.16.
Before placing concrete, thoroughly clean all forms and structural steel that contact the concrete and ensure that the space to be occupied by the concrete is free of laitance, silt, dirt, shavings, sawdust, loose and built-up rust, and other debris.
Deposit concrete using methods that ensure reinforcing steel is completely enveloped in concrete mortar and that allow inspection of concrete enveloping the reinforcing steel. Use a method or device to convey the concrete from the mixer to the work that prevents coarse aggregate separating from the mortar. If depositing concrete in shallow members, such as slabs, place it with as short a vertical drop as possible. Place the concrete over a section to maintain a practically horizontal surface. If using a chute, slope the chute to allow concrete to flow without segregation. Place concrete as near as possible to its final position.
Drop concrete into the forms with a free-fall distance of 5 feet (1.5 m) or less. As necessary, use drop chutes to limit the free fall to 5 feet (1.5 m) and to ensure the delivery ends as vertical as possible.
Place concrete in structures using vibration. Furnish and use sufficient vibration equipment of the type and size approved by the Engineer to properly compact the concrete immediately after it is placed in the forms. The vibrators shall generally be of a type that is applied directly to the concrete and have a frequency of at least 4500 impulses per minute. If the concrete is inaccessible for this method of vibration, apply the vibrators to the outside of the forms.
Do not move concrete using a vibrator. Vibrate freshly deposited concrete at the point deposited. Slowly insert and withdraw the vibrators vertically into the concrete until the concrete is thoroughly compacted but not segregated. During vibration, do not disturb partially hardened concrete.
As necessary, spade along form surfaces, in corners, and in locations impossible to reach with vibrators to ensure smooth surfaces and dense concrete. Closely observe the results obtained on the first concrete placed, and, if necessary, modify the mix according to this specification to secure the best results.
511.11 Slipform Construction of Bridge Railing. If Class HP concrete is specified, the Contractor may replace up to two-thirds of the No. 8 size coarse aggregate with No. 57 size coarse aggregate. The Engineer will submit the approved slipform concrete mix design to the Laboratory for record purposes.
If slipforming, provide finished concrete conforming to the following tolerances from plan dimensions:
|
Reinforcing steel cover |
-1/2 inch, +1/2 inch (-13 mm, +13 mm) |
|
Top width dimension |
-0, +1/4 inch (+6 mm) |
|
Bottom width dimension |
-0, +1/2 inch (+13 mm) |
|
Surface flatness |
1/4 inch in 10 feet (6 mm in 3 m) |
|
Vertical alignment (Deviation from a line parallel to the grade line) |
1/2 inch in 20 feet (13 mm in 6 m) |
Tie all joints and splices in bridge railing reinforcing steel. Before placing concrete, perform a slipforming dry run to verify reinforcing clearance and rigidity of the reinforcing cages. Adjust and stabilize the cage as necessary to establish the required clearances and to ensure the cage will not move during slipforming. The Contractor may add any additional diagonal reinforcing steel between the front and rear vertical reinforcing faces to establish the required rigidity.
Repair or patch honeycombing, cracking, tearing, and other defects immediately after concrete exits the slipform equipment. Completely fill defects with concrete without using water to smooth or close the surface.
After the concrete initially sets, but before any shrinkage cracks develop, saw control joints 1 1/4 inches (32 mm) deep into the perimeter of the parapet. Generally, initial set is within 6 hours of batching of the concrete. Ensure that all joints are sawed within 24 hours of placement. Saw control joints using an edge guide, fence, or jig to ensure that the joint is straight, true, and aligned on all faces of the parapet. The joint width shall be the width of the saw blade, a nominal 1/4 inch (6 mm). Caulk the control joints with a polyurethane or polymeric material conforming to ASTM C 920, Type S.
Slip formed concrete requires different slumps than those listed in Item 499 or other plan specified concrete. Provide a slump such that the concrete exiting the slipform does not pull but is stiff enough to prevent waviness and sags in the finished surfaces. Cure slipform concrete according 511.17, Method A. Because slipformed concrete has a low water-cement ratio, timely application of the water cure is critical in helping control shrinkage cracks.
Furnish platforms as necessary to protect traffic passing under the bridge from falling debris during the slipforming operation, to allow access for completing the finishing operation, and to allow the Engineer access to the outside of the parapet.
The Engineer will inspect the slipformed surface for horizontal cracking no earlier than 21 days after completion of the slipforming operation. Repair all horizontal cracks by epoxy injection. If a concrete sealer was applied, repair damage to the sealer after completing the epoxy injection.
511.12 Construction Joints. If construction joints are shown on the plans, place all concrete between consecutive joints in a continuous operation. Do not place concrete against a joint for at least 12 hours, or as required by 511.17.
Obtain the Director’s approval before placing any construction joint not shown on the plans or required by 511.10.
Before placing concrete, determine the location where the day’s concrete placing ends. If practical, end placing the day’s concrete perpendicular to the lines of principal stress and in regions of small shear. Do not install horizontal joints in concrete girders and beams.
Form construction joints using bulkheads with keyways. Locate keyways clear of exposed surfaces by approximately one-third the thickness of the joint.
Where practical, avoid horizontal joints in piers, abutments, and retaining walls, otherwise locate horizontal joints 2 feet (0.6 m) or more above the normal water level.
For construction joints not shown on the plans and above ordinary low water, in abutments, and in retaining walls that retain earth fills, install a 36-inch (1 m) strip of Type B waterproofing according to Item 512 to the back of the joint.
Avoid joints in cantilevered members.
Dampen the surface of the concrete of the horizontal construction joints immediately before placing adjoining concrete.
Place and protect horizontal construction joints between bridge slabs and superimposed curbs, parapets, sidewalks, and median strips in the same manner as the remainder of the slab. Cure the construction joints according to 511.17.
Avoid disturbing the bond between protruding reinforcing steel and the deck concrete. If using the curb areas to place the deck, tie and brace the reinforcing steel to prevent its movement.
Where walls or columns support slabs or beams, place concrete in wall or column to the bottom of the slab or beam and allow the concrete to settle for at least 2 hours before placing concrete in the slab or beam.
511.13 Work Stoppage. If the work is unexpectedly interrupted by breakdowns, storms, or other causes, rearrange the freshly deposited concrete to provide a suitable construction joint. If this joint occurs at a section with shear stress, prevent a plane of weakness by providing an adequate mechanical bond across the joint by forming a keyway, inserting reinforcing steel, or by some other means satisfactory to the Engineer.
511.14 Depositing Concrete Under Water. Except for cofferdam seals and drilled shafts, do not place concrete under water.
511.15 Depositing and Curing Concrete During Cold Weather. If placing concrete when the atmospheric temperature is 32 °F (0 °C) or less, or if weather forecasts predict these temperatures during the curing period, follow the procedures of this subsection.
Heat the water or aggregate, or both, as necessary to produce concrete with a temperature when placed of at least 50 °F (10 °C) but not greater than 70 °F (21 °C).
Place concrete against materials with a temperature of greater than 32 °F (0 °C). If necessary, heat the forms, reinforcing steel, and foundation materials before placing the concrete.
Maintain the concrete surface temperature between 50 and 100 °F (10 and 38 °C) for a period of not less than 5 days, except as modified in 511.15.C. After the minimum cure period of 5 days, reduce the concrete surface temperature at a rate not to exceed 20 °F (11 °C) in 24 hours until the concrete surface temperature is within 20 °F (11 °C) of atmospheric temperature.
Install sufficient high-low thermometers to readily determine the concrete surface temperature. For deck slabs, install high-low thermometers to measure deck bottom surfaces, deck fascia surfaces, and deck top surfaces.
Maintain the concrete curing temperature using a heated enclosure, insulated forms, or by flooding, except cure deck slabs less than 10 inches (250 mm) thick using more than just insulated forms.
Remove falsework and open cold weather concrete to traffic according to 511.17.
A. Heated Enclosure. Construct the heated enclosure to surround the top, sides, and bottom of the concrete. Construct strong and wind proof enclosures that contain adequate space to allow free circulation of air around the forms and concrete.
Before placing concrete, construct the enclosure and heating devices to the extent allowed by the concrete operation. As the concreting operation progresses and as soon as possible after placing concrete, complete construction of the enclosures and apply heat. Supply heat by a method that continuously maintains a reasonably uniform temperature throughout the enclosures and does not discolor the concrete.
Vent combustion-type heating devices outside the enclosure.
If dry heat, other than free steam, maintains the enclosure temperature, immediately cover exposed concrete with two thicknesses of burlap. Continuously wet the burlap and, except for required rubbing of the concrete, do not remove the burlap during the heating period.
If wood forms without liners are left in place more than 2 days after the placing of concrete, thoroughly wet the forms at least once each day for the remainder of the heating period. If forms are removed during the heating period, thoroughly drench the concrete with water and, for the remainder of the heating period, cover and wet the concrete with burlap as specified above.
B. Insulation. Install sufficient thermometers to readily determine the concrete surface temperature. If the surface temperature approaches 100 °F (38 °C), loosen or otherwise vent the forms or insulation to keep the surface temperature within the limits specified above. If insulation does not maintain the minimum required temperature, promptly enclose the concrete as specified in 511.15.A or flood the concrete as specified in 511.15.C.
Use a wind and water resistant insulating material. Ensure edges, corners, and other points of extreme exposure are adequately insulated. Place a tarpaulin or other Engineer approved waterproof cover over the insulation to protect the concrete top surface.
C. Flooding with Water. The Contractor may flood the concrete with water provided flooding does not damage the concrete. Heat the water to a temperature from 50 to 100 °F (10 to 38 °C). The Contractor may stop using heated water after 48 hours if the concrete remains flooded to a depth of 1 foot (0.3 m) above its highest elevation for at least the next 120 hours.
511.16 Removal of Forms. To facilitate finishing, remove forms from vertical surfaces that receive a rubbed surface finish as soon as the concrete has hardened sufficiently that rubbing will not damage it.
511.17 Curing and Loading. Remove falsework and open structures to traffic after the concrete has cured for the time specified by Table 511.17-1.
|
|
Span[1] |
Age of Concrete in Days |
|
|
No Beam Test |
Beam Test [2] |
||
|
Removing Falsework |
Over 10 feet (3 m) |
14 |
5 |
|
10 feet (3 m) or less and all pier caps |
7 |
3 |
|
|
Traffic [3] |
Any |
14 |
7 |
|
[1] Span is defined as the horizontal distance between faces of the supporting elements when measured parallel to the primary reinforcement. |
|||
|
[2] Applicable only when the average modulus of rupture for two tests is not less than 650 psi (4.5 MPa). |
|||
|
[3] When placing Class HP concrete for a superstructure between October 15 and March 15, open the deck to traffic no sooner than 30 days after placement. |
|||
If the air temperature surrounding the concrete is maintained between 32 and 50 °F (0 and 10 °C), and if the provisions of 511.15 do not apply, maintain the concrete above 32 °F (0 °C) for 7 days or until a successful beam test, except this time shall not be less than 5 days.
If a beam test is not performed, maintain the air temperature surrounding the concrete above 50 °F (10 °C) for 7 days. Extend the 7-day period and the times for removing falsework and opening to traffic one hour for each hour the temperature of the air surrounding the concrete is below 50 °F (10 °C) and until the concrete has experienced 7 days, or 168 hours, of temperature above 50 °F (10 °C). Cure concrete as follows:
|
Location |
Curing Method [1] |
|
Superstructure concrete |
Method A |
|
Concrete to which sealer is applied |
Method A |
|
Construction joints |
Method A |
|
Top surface of Class HP concrete deck superstructure concrete |
Method A followed by Method B |
|
Concrete with waterproofing |
Method A or Method B |
|
All other concrete |
Method A or Method B |
|
[1] Method A is water curing. Method B is membrane curing. If using Method B on areas to be waterproofed, remove the curing membrane. |
|
Do not install compression rings on pier columns or similar items of construction for supporting falsework or subsequent construction until after a 72-hour curing period.
Do not apply loads to or perform work on new concrete until workers and materials will not damage the concrete or interfere with its curing. Allow at least 36 hours or until the average of two beam tests is greater than 650 pounds per square inch (4.5 MPa) before working on new concrete, but do not interfere with curing of new concrete.
Concrete curing methods are as follows:
A. Method A, Water Curing. With the exception of the top surface of deck superstructure concrete, protect surfaces not covered by forms immediately after final finishing with two thicknesses of wet burlap. Keep burlap wet for at least 7 days by the continuous application of water. If forms are removed before 7 days, immediately drench the exposed concrete with water and cover it with burlap. Continuously apply water to the burlap for the remainder of the curing period.
Instead of continuous application of water, with the exception of the top surface of deck superstructure concrete, the Contractor may cover the wet burlap with white polyethylene sheeting or plastic coated burlap blankets conforming to 705.06. Place plastic coated burlap blankets wet and with the burlap side against the previous layer of wet burlap. Sufficiently lap and secure adjoining plastic coated blankets or polyethylene sheets at the laps and edges to form a seal that maintains the concrete wet at laps and edges. Cover white polyethylene sheeting or plastic coated blankets containing holes or tears with an additional covering of plastic sheeting or blankets as directed by the Engineer.
Cover the top surface of deck superstructure concrete with a single layer of clean wet burlap after it is bullfloated if necessary, and finished. Keep the burlap wet by a continuous flow of water through soaker hoses and cover the hoses with a 4 mils (100 mm) white opaque polyethylene film for 7 days. After 7 days, allow the surface of the deck to dry.
After curing the top surface of Class HP deck superstructure concrete for 7 days, remove the burlap and standing water. Within 12 hours after removing the burlap, apply a curing membrane and cure the concrete according to Method B.
B. Method B, Membrane Curing. Immediately after the free water has disappeared on surfaces not protected by forms, apply curing material conforming to 705.07, Type 1 or 1D. If forms are removed before the end of the 7-day curing period, apply curing material on the concrete exposed by removing the forms.
Thoroughly agitate curing material immediately before use. Apply the membrane curing material at the rate of at least 1 gallon per 200 square feet (1 L/5 m2) of surface and in a fine mist to provide a continuous, uniform, and water impermeable film without marring the concrete surface. If the film is broken or damaged during the specified curing period, apply curing material as specified above to the damaged or affected areas.
Do not allow workers, materials, and equipment on the concrete during the curing period, unless adequately protecting the membrane curing material from damage.
511.18 Surface Finish. Immediately after removing forms, clean, dampen, and fill with mortar all cavities produced by form ties, honeycomb spots, broken corners or edges, and other defects. Use a mortar of the same proportions used in the concrete being finished. Substitute sufficient white cement for the regular cement in the mortar used to fill holes and perform other corrective work to produce finished patches of the same color as the surrounding concrete. Finish other contiguous exposed surfaces on the structure in a similar manner and to the extent required to produce a uniform appearance.
On all exposed surfaces, remove fins and irregular projections with a stone or power grinder, taking care to avoid contrasting surface textures.
A. Grout Cleaning. If grout cleaning is shown on the plans or necessary for corrective work, wet the concrete surface and then uniformly cover the concrete with a grout consisting of one part cement, 1 1/2 parts fine sand conforming to 703.03, and sufficient water to produce a mortar with the consistency of thick paint. In the quantity determined by the Engineer necessary to match the color of the concrete, use white portland cement in the grout. uniformly apply the grout with brushes or spray guns, completely filling air bubbles and holes. Immediately after applying the grout, vigorously scour the concrete surface with a cork or other suitable float. While the grout is still in a plastic condition and while the grout does not pull from the holes or depressions, finish the surface with a sponge rubber or other suitable float, removing excess grout. After the grout thoroughly dries, vigorously rub the surface with a dry burlap, removing dried grout until there is no visible film of grout remaining on the surface. Perform the entire cleaning operation of each area on the same day. Remove dark spots or streaks that remain after the cleaning operation using a fine grained silicon carbide stone. Stop rubbing with the silicon carbide stone before the surface texture changes. Unless otherwise directed by the Engineer, perform grout cleaning during the final project clean up.
B. Rubbed Finish. If a rubbed finish is shown on the plans, if possible, remove forms within 2 days after placing concrete. Finish the surface as specified above to correct defects. After the mortar used for finishing is thoroughly set, and for a minimum of 2 hours before starting the rubbed finish, thoroughly saturate the concrete with water.
Rub surfaces to be finished with a medium coarse silicon carbide stone until all form marks, projections, and irregularities are removed, all voids are filled, and a uniform surface is obtained. Leave the paste produced by rubbing in place. Other than water, do not apply additional material to the surface. After placing concrete above the finishing area, obtain the final finish by rubbing the concrete with a fine silicon carbide stone and water until the entire surface is of a smooth texture and uniform in color. Protect surfaces with a rubbed finish from damage caused by subsequent construction operations. If damaged, clean and refinish the surface as specified above.
511.19 Roadway Finish. Finish and test concrete deck slabs according to 451.12. Do not groove or broom finish a strip of surface 9 to 12 inches (220 to 300 mm) wide adjacent to curbs and barriers. Provide a broom drag finish on concrete deck slabs in the longitudinal or transverse direction.
The Engineer will approve the finishing machine. Provide a self-propelled machine with forward and reverse drive mechanisms that enable precise control of machine velocity in both directions. The machine shall have two rotating rollers, leveling augers, and either a vibrating pan or vibrating rollers. Furnish the Engineer documentation that verifies the machine is capable of varying the vibrating frequency for pans or rollers from 1500 to 5000 pulses per minute. Do not use vibrating rollers that have fins protruding more then 1/4 inch (6 mm) from the roller. Use a finishing machine capable of finishing transversely while traveling in both directions across the deck. Provide screeds capable of rising above the concrete surface. Provide a finishing machine capable of finishing the full width of the decks between curbs or parapet walls. The wheels of the finishing machine shall run on temporary riding rails adequately supported on the structural steel or falsework of the deck. Make the rail and rail supports of steel and arrange the rail and rail supports so that the weight of the finishing machine and the operator cause zero vertical deflection while traveling across the deck. Ensure the rail is straight, with no sections exceeding a tolerance of 1/8 inch in 10 feet (3 mm in 3 m) in any direction. Elevate support rails a sufficient distance above the slab to allow the simultaneous hand finishing of areas not machine finished. Fabricate and install rail supports to allow removal to at least 2 inches (50 mm) below the top of the slab. Fill holes formed by the removal of rail supports during the final finishing of the slab. Deliver and distribute the concrete at a uniform and adequate rate no more than 10 feet (3 m) directly in front of the finishing machine by suitable mechanical equipment.
511.20 Bridge Deck Grooving. After Class S concrete has cured, saw transverse grooves into the deck.
After water curing Class HP concrete and either before applying curing compound or some period after applying curing compound and before opening the bridge to traffic, saw transverse grooves into the deck. If sawing grooves after applying the curing compound, and concrete deck is less than 30 days old, reapply the curing compound after removing standing water, within 12 hours after sawing grooves in the deck.
The grooving of both Class S concrete and Class HP concrete shall be performed as specified below.
Use diamond blades mounted on a multi blade arbor on a self-propelled machine that was built for grooving of concrete surfaces. The groove machine shall have a depth control device that detects variations in the pavement surface and adjusts the cutting head height to maintain the specified depth of the groove. The grooving machine shall have devices to control alignment. Do not use flailing or impact type grooving equipment.
Begin and end grooves 9 to 12 inches (220 to 300 mm) from curbs, parapet toes, or deck edges, and saw grooves perpendicular to the bridge centerline.
Provide an experienced technician to supervise the location, alignment, layout, dimension, and grooving of the surface.
Saw grooves in a continuous pattern across the surface. Stop sawing 9 to 12 inches (220 to 300 mm) from any device in place in a bridge deck, such as scuppers or expansion joints. Stop sawing 2 inches to 2 feet from skewed expansion joints. Saw grooves in a random pattern spaced at 3/8 to 1 3/4 inch (10 to 45 mm), with 50 percent of spacings less than 1 inch (25 mm). Saw grooves approximately 0.15 inches (4 mm) deep and 0.10 inches (3 mm) wide.
At the beginning of each work shift, furnish a full complement of grooving blades with each saw that are capable of cutting grooves of the specified width, depth, and spacing.
If during the work, a single grooving blade on a machine becomes incapable of cutting a groove, continue work for the remainder of the work shift. The Contractor is not required to cut the groove omitted because of the failed blade. Should two or more grooving blades on a machine become incapable of cutting grooves, cease operating the machine until it is repaired.
Continuously remove all slurry and remaining residue from the grooving operation and leave the deck surface in a clean condition. Prevent residue from grooving operations from flowing across shoulders or across lanes occupied by public traffic or from flowing into gutters or other drainage facilities. Remove solid residue before the residue is blown by passing traffic or by wind.
Provide water as necessary to saw grooves according to this subsection.
511.21 Sidewalk Finish. After placing, strike off the concrete with a template and finish the concrete with a float to produce a sandy texture.
511.22 Sealing Joints and Cracks. After completing all curing operations and allowing the deck to thoroughly dry, seal the following areas with a high molecular weight methacrylate (HMWM) sealer as specified in Item 512 before opening the deck to traffic:
A. Transverse joints in the deck.
B. Joints between the concrete deck and steel end dams.
C. Longitudinal joints in the deck.
D. Longitudinal joints between the deck and safety curb, barriers, and parapets, etc.
E. Cracks discovered in the deck that will be checked on the top and bottom surface before opening the deck to traffic.
511.23 Class HP Concrete Testing. If included as a separate pay item, perform the following tests on the concrete.
A. Rapid Chloride Permeability Tests. Perform test according to AASHTO T 277. Take a minimum of three tests for decks containing less than 100 cubic yards (75 m3) of superstructure concrete. For all other decks, take six tests. Test deck superstructure concrete samples obtained from the actual concrete used.
Provide the Engineer with results of rapid chloride permeability tests at 28, 56, and 90 days.
B. Drying Shrinkage Tests. Perform test according to ASTM C 157 and at the frequency specified for rapid chloride permeability tests.
Provide the Engineer with results of drying shrinkage tests at 4, 7, 14, 28, 56, and 90 days.
C. Heat of Hydration Testing. Perform testing to determine the potential for length change due to thermal expansion and contraction. Immediately after placing the deck, install three thermometers into the fresh concrete at a location that is accessible for readings and representative of the overall deck pour. Locate the thermometer bulbs at 1 inch (25 mm) below the surface of the concrete, at approximately mid-slab, and at 1 inch (25 mm) above the bottom deck form. Leave the thermometers in place throughout the testing time. The Contractor may lubricate and place the thermometers in a thin plastic sheath to facilitate eventual removal.
Record temperatures at the following intervals:
|
Test Intervals |
Time |
|
2 hours |
first 12 hours |
|
3 hours |
second 12 hours |
|
4 hours |
second day |
|
8 hours |
third thru fifth day |
Record ambient air temperatures when taking concrete temperatures. Ensure that all testing is performed by a testing laboratory regularly inspected by the Cement and Concrete Reference Laboratories (CCRL). Furnish a copy of the last CCRL inspection report to the Engineer before the test slab pour.
If the Contractor uses Class HP 1 or 2 for parapets or substructures, perform three additional chloride permeability and drying shrinkage tests for the parapets or substructure concrete. If used for parapets, perform a heat of hydration test as described above with one thermometer located at 1 inch (25 mm) below the top of the parapet and a second thermometer located 19 inches (500 mm) below the top of the parapet, approximately midway between the front and back faces of the parapet. The Engineer will not require additional testing for units constructed with the same concrete mix option as the deck.
Tabulate test results on the attached form and forward the form to the Laboratory no later than 10 days following the completion of the tests.
After removing thermometers, drill out and fill the holes as approved by the Engineer.
511.24 Method of Measurement. The Department will measure the appropriate concrete item by the number of cubic yards (cubic meters) determined by calculations from plan dimensions, in place, completed and accepted.
The Department will not make deductions for the volume of the reinforcing steel, conduits, or structural steel other than beam flanges embedded in deck slabs. The Department will not make deductions for the volume of embedded timber or concrete piles.
Superstructure concrete includes the concrete in deflective parapets not having a metallic railing.
The Department may measure deck concrete by either volume or area using plan dimensions.
511.25 Basis of Payment. The Department will not pay for Class HP concrete Testing until the Laboratory receives all test results.
The Department will not pay for additional test slabs resulting from proportioning or batching sequence modifications for the Class HP.
If the contractor elects to use high early strength concrete, the Department will not pay additional costs associated with the use of these materials even if use is desirable to expedite the work.
The Department will not pay for additional reinforcing steel required to adequately stabilize the cages.
The Department will not pay for repairs to horizontal cracks by epoxy injection or, if a concrete sealer was applied, for repairs to the sealer after the completing the epoxy injection.
The Department will not pay extra for any type of surface finish specified in 511.18, the cost being considered as included in the price bid for concrete.
If the Contractor elects to saw the deck after applying the curing compound, the Department will not pay to reapply the curing compound.
All costs for sealing as specified in 511.22 is incidental to the appropriate concrete item. The Department will not make separate payment for sealing.
The Department will pay for accepted quantities at the contract prices as follows:
Item unit Description
511 Cubic
Yard Class ___
Concrete, ___
(Cubic Meter)
511 Cubic
Yard Class S Concrete,
Bridge Deck
(Cubic Meter)
Square Yard
(Square Meter)
511 Cubic
Yard Class HP,
(Cubic Meter)
511 Square
Yard Class HP,
(Square Meter)
511 Cubic
Yard Class HP,
(Cubic Meter)
511 Cubic
Yard Class HP,
Concrete Substructure
(Cubic Meter)
511 Lump Sum Class HP Concrete Test Slab
511 Lump Sum Class HP Concrete Testing